Radiology (Medical Imaging)
What is Radiology
Radiology is a field in medicine where doctors use various imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, MRI or angiography to look at the inside of human body in order to find out the cause of illnesses. Usually a radiographer operates the machine to obtain the images and a radiologist study the images and issue a clinical report.
A radiologist is a fully qualified doctor who has undergone 5 years of post-graduate specialist training in diagnostic radiology and obtained the Fellowship of the Royal College of Radiologists (FRCR).
Interventional radiology is a subspecialty of radiology. An interventional radiologist treats medical conditions using keyhole surgical technique with the guidance of imaging.
What is Radiology
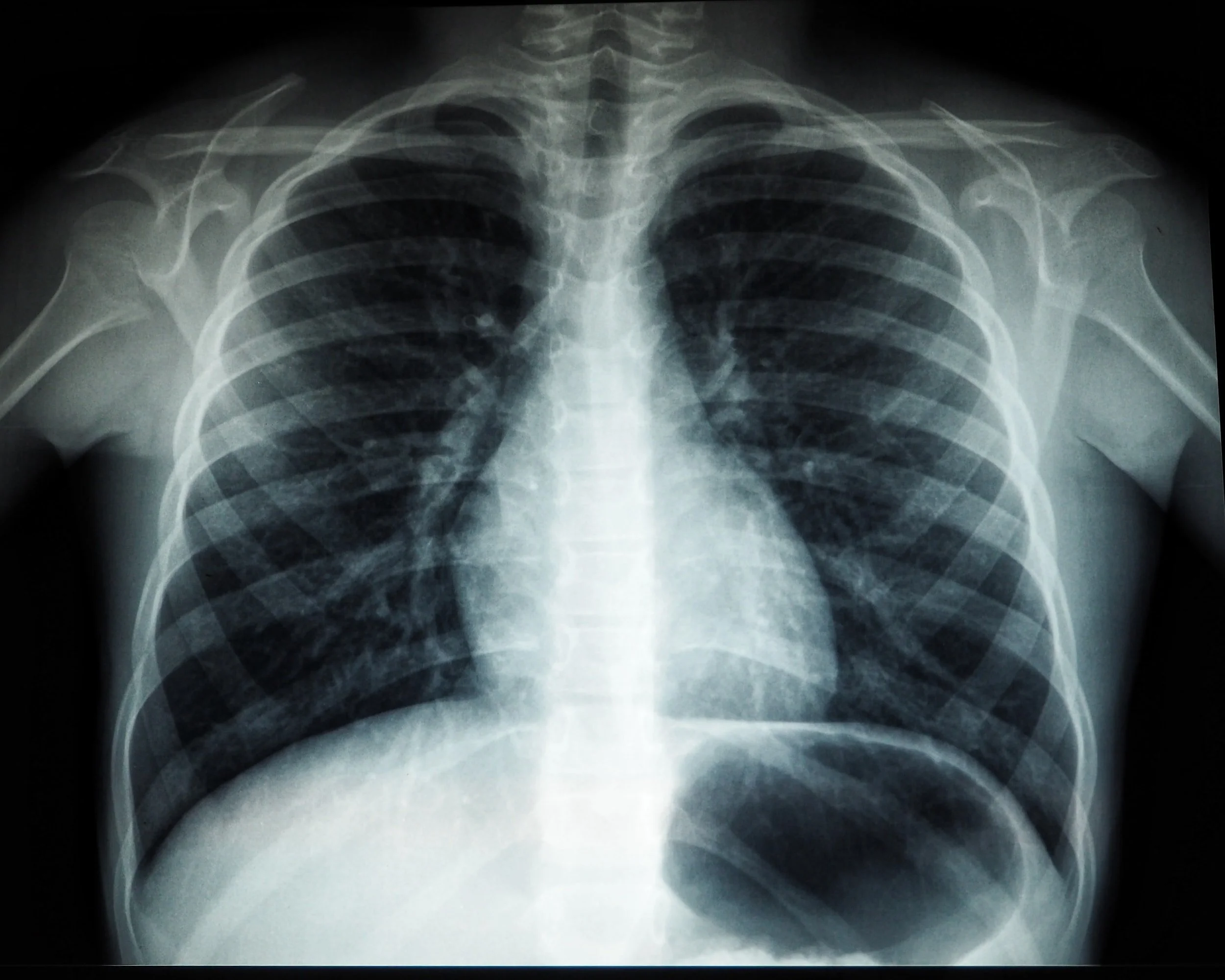
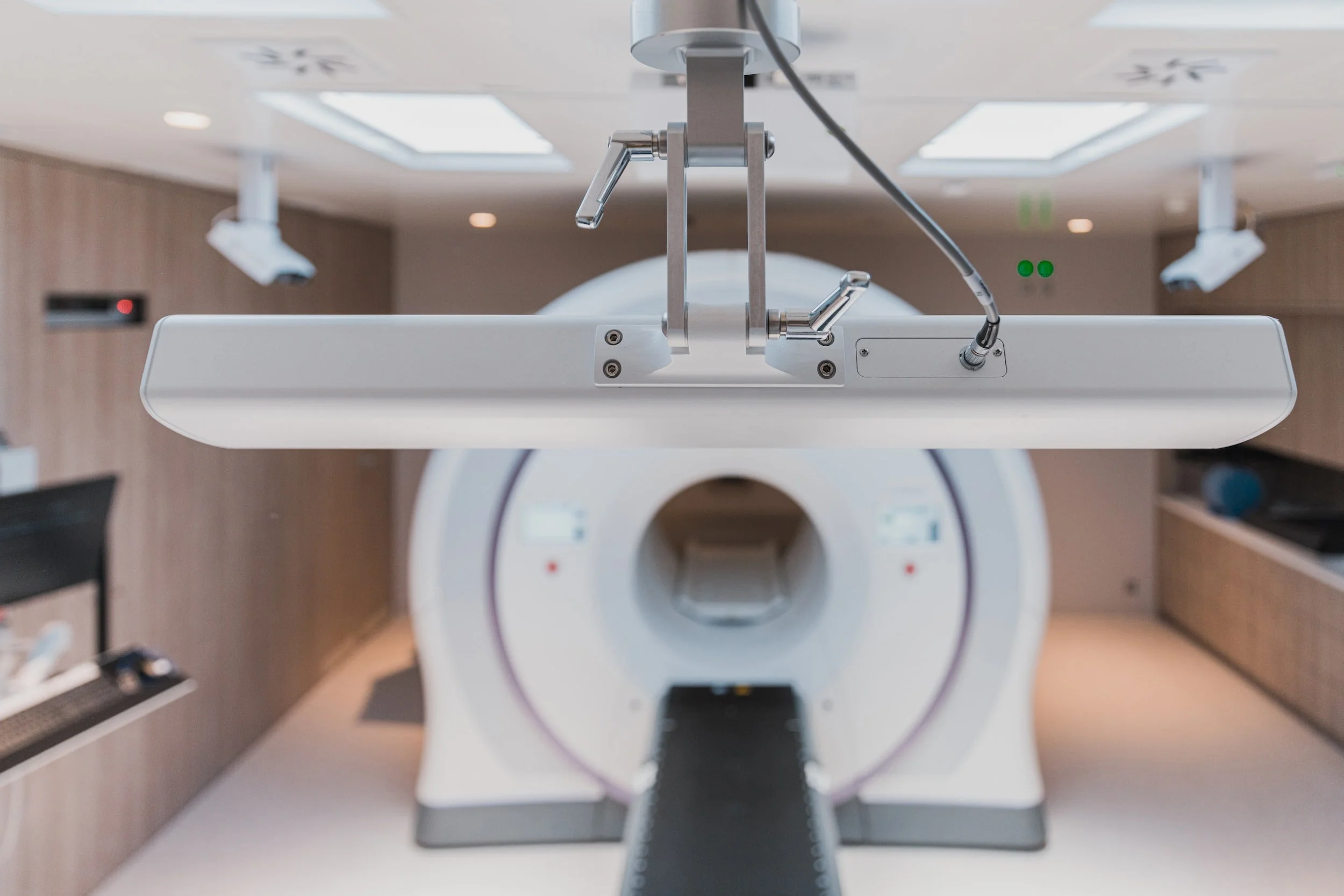
Diagnostic Radiology
Diagnostic radiology is the use of imaging techniques to look inside the human body to find out the cause of illnesses.
X-Ray - This is the oldest technique where beams of x-ray are made to pass through the human body and then fall onto a film or sensor, creating an image based on how much x-ray is blocked or deflected and not reaching the film or sensor.
CT Scan - This is a derivative of x-rays where many x-ray images are put together by computer to create a more detailed 2D and 3D images. This is the scan where patients are put through a donut shaped machine.
MRI - A imaging technique using magnetic field rather than x-ray. MRI machine is more like a tunnel rather than donut. It is good at looking at certain abnormalities and it complements, but does not replace CT scan.
Angiography - Contrast is injected into an artery or vein and live images of the flow are then obtained. This is different from CT angiography or MR angiography where contrast is injected into a small vein remote to the site of interest and static images were obtained using CT and MR techniques.
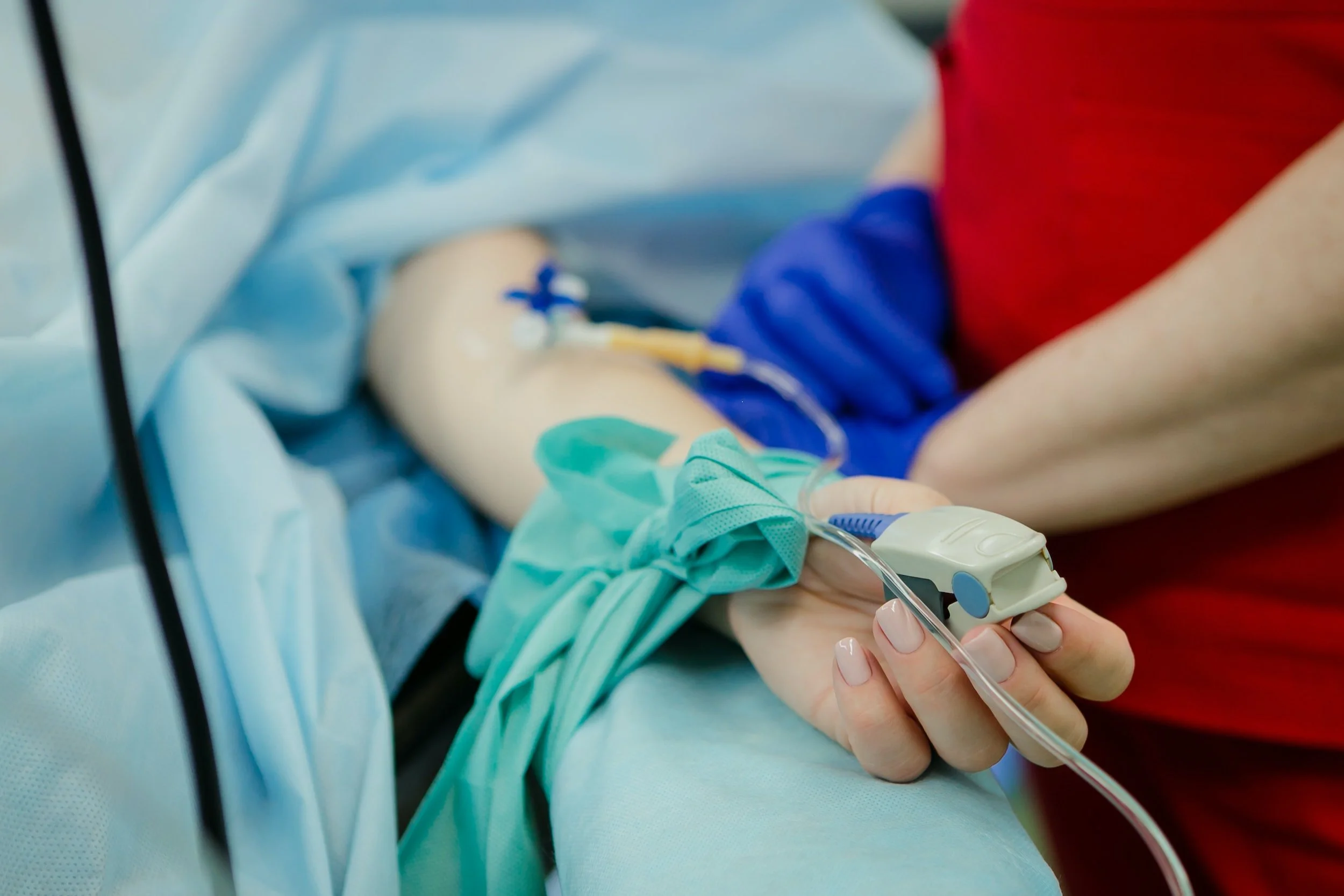
Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology, also called image guided surgery, is a specialist field within radiology where minimal invasive procedures are performed with help of x-ray or CT, either to provide treatment or to get more information for diagnostic purpose.
Examples of procedures performed for diagnostic purposes include liver biopsy, kidney biopsy and biopsy of any abnormal tissue seen on CT or ultrasound.
Examples of treatment procedures include balloon angioplasty of arteries, venoplasty of veins, stopping bleeding, vascular access and drainage of infective collection.
These are often done as day case under local anaesthesia or sometimes with sedation.